Gross U.S. Federal Debt as percent of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) hit 105% in 2018, the highest since 1946.
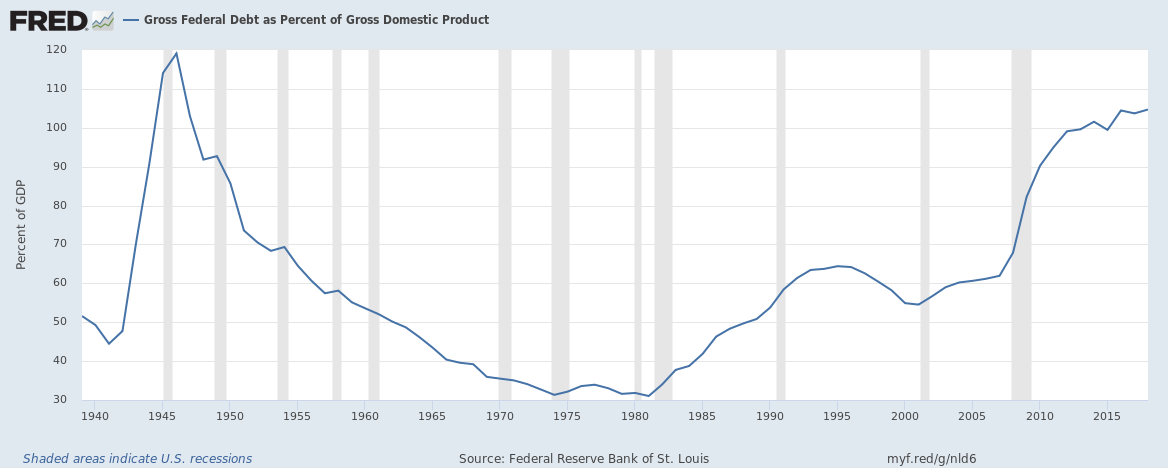
Continue reading “U.S. Federal Debt hit 105% of GDP in 2018, the highest since 1946 but …”
Why wouldn’t it be?
Gross U.S. Federal Debt as percent of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) hit 105% in 2018, the highest since 1946.

Continue reading “U.S. Federal Debt hit 105% of GDP in 2018, the highest since 1946 but …”
The 1980s was the Japanese decade with Japanese companies being the most valuable ones in the world and Japan being at the centre of the global economic growth. But since the 1990s, Japan has struggled with growth and deflation.
The answer is different on how you look at it – in terms of absolute outstanding debt, growth rates and relative to GDP.
In absolute terms the total credit market or total debt outstanding of the U.S. which includes debt owed by the government (Federal and local), corporations and households stands at $72 trillion.
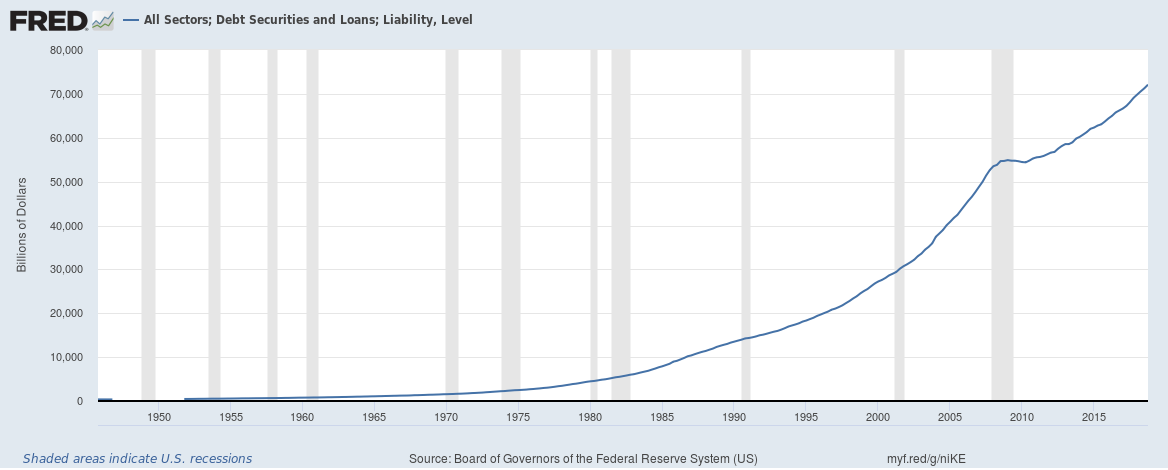
Continue reading “How big really is the total debt of the United States?”
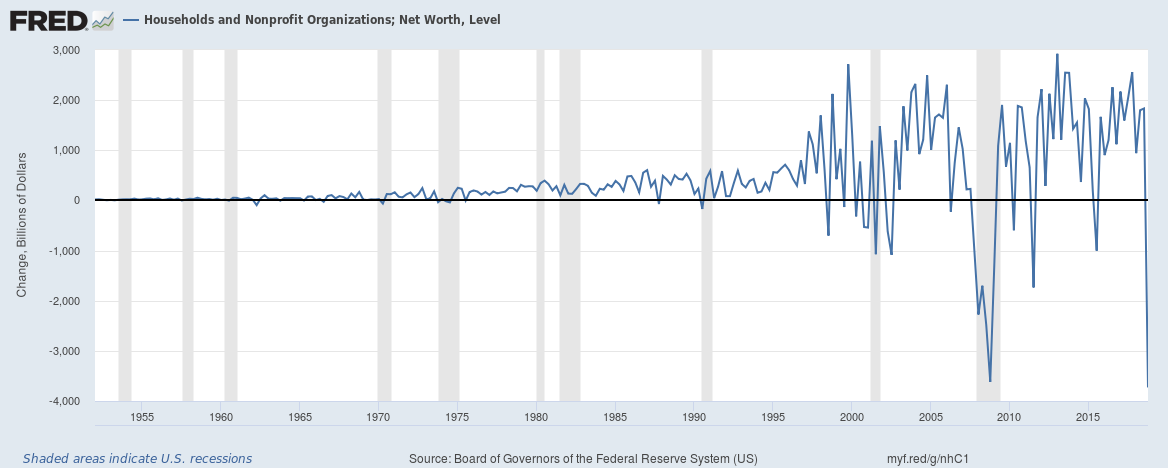
Household wealth (or household net worth) in the United States fell by a record $3.72 trillion in the fourth quarter of 2018. The fall in the stock markets would have probably been the largest contributor to the overall fall.
The Governing Council of the European Central Bank (ECB) expects the key ECB interest rates to remain at their present levels at least through the end of 2019.
The interest rate on the main refinancing operations and the interest rates on the marginal lending facility and the deposit facility are 0.00%, 0.25% and -0.40% respectively and these rates are expected to remain in place at least until the end of 2019.
Real gross domestic product (GDP) for the United States increased at an annual rate of 2.6% in Q4 2018, according to the initial estimate released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).

Continue reading “U.S. Q4 2018 GDP growth estimated at 2.6%; 2018 GDP growth at 2.9%”
We wrote recently that delinquency and charge-off rates across banks in the United States remain low and that bad loans aren’t really increasing for banks in the United States despite some claiming that they are. We had also written about banks in the United States having a problem – they couldn’t find enough customers to lend money to. We wrote that last year and it appears a few things are changing; bank lending in the U.S. is now finally on the up.
Continue reading “Have banks in the U.S. started lending more money recently?”
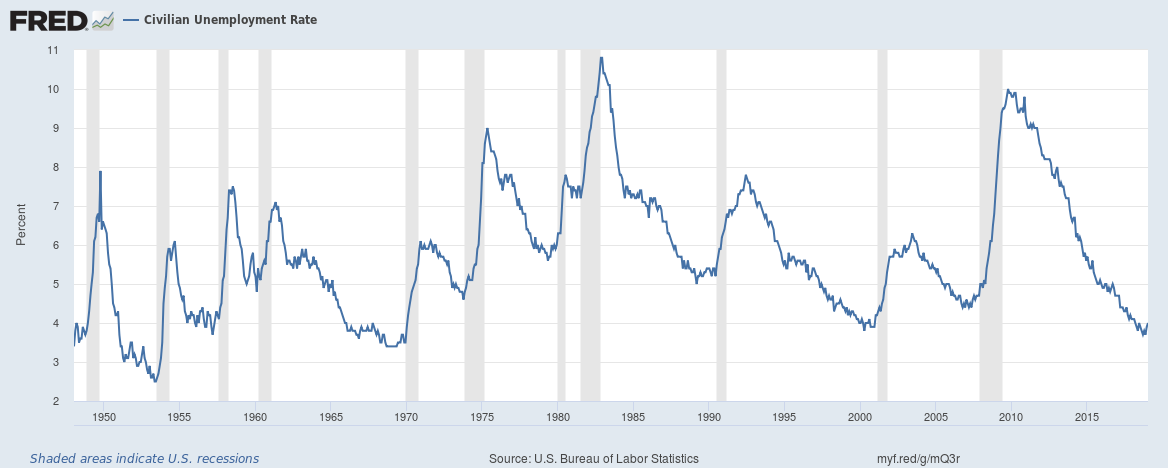
This is an interesting one, one of our three U.S. recession indicators is the U.S. unemployment rate.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics data reveals that the U.S. unemployment rate has hit a new multi-year low four to eight months before the start of every recession since the 1940s. In other words, the economy hits full employment four to eight months before the start of a recession.
The unemployment rate goes up at least 1% and then doesn’t go back down without a recession occurring.
The Baltic Dry Index is a trade indicator that measures shipping prices of major raw materials and is often seen as a global growth indicator. The index is based on a daily survey of agents all over the world.
The Baltic Dry Index is down 48% over the past month (and down 47% over the past year). Is this an indicator of more trouble around global growth?
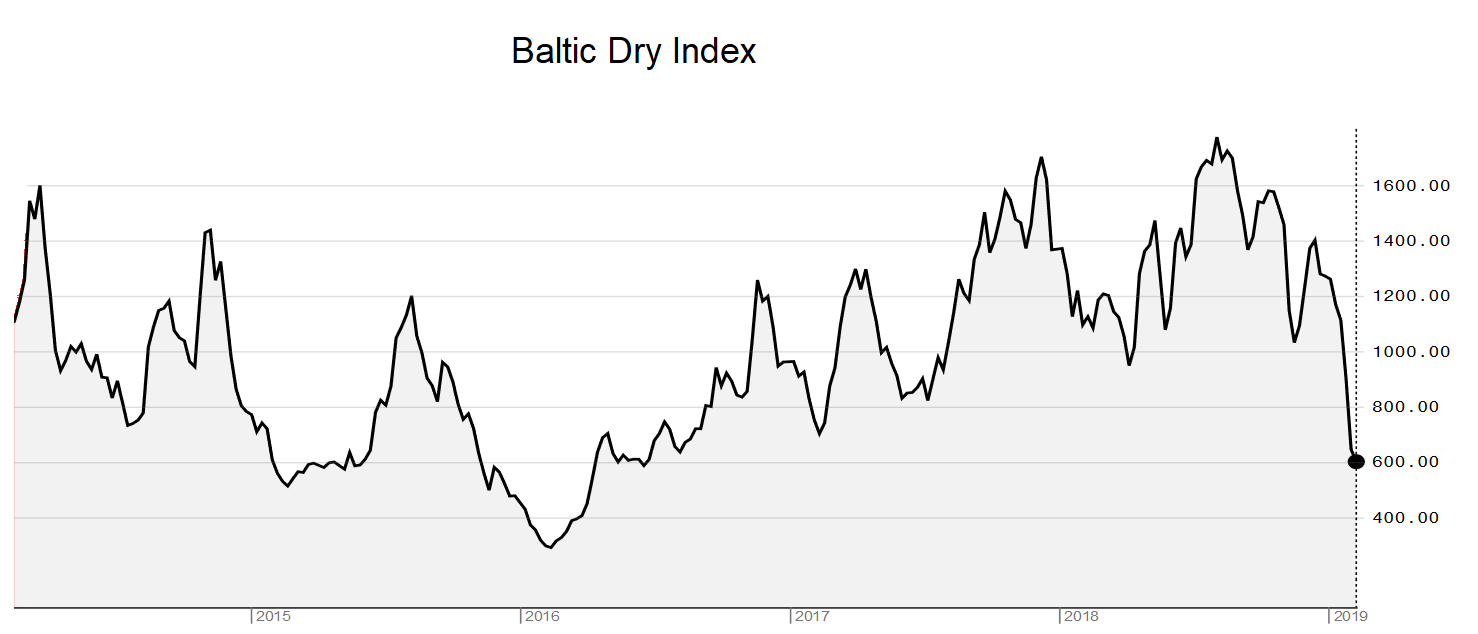
Continue reading “The Baltic Dry Index is down 48% over the past month”